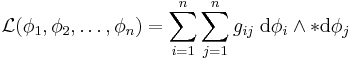Sigma model
In physics, a sigma model is a physical system that is described by a Lagrangian density of the form:
Depending on the scalars gij it is either a linear sigma model or a non-linear sigma model. The fields 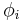 , in general, provide a map from a base manifold called the worldsheet and a target (Riemannian) manifold that is often understood to be the spacetime.
, in general, provide a map from a base manifold called the worldsheet and a target (Riemannian) manifold that is often understood to be the spacetime.
A basic example is provided by quantum mechanics which is a quantum field theory in one dimension. It's a sigma model with a base manifold given by the real line parameterizing the time (or an interval, or the circle, etc.) and a target space that is the real line.